細(xì)胞組織消化常用的幾種酶的選擇
 |
|
直接從生物體獲取的組織,一般需要將其消化成單個(gè)細(xì)胞才能進(jìn)行體外培養(yǎng)。這種直接從離體組織獲得的細(xì)胞,更接近于生物體內(nèi)的生活狀態(tài),且生物性狀尚未發(fā)生很大改變,因此在藥物篩選、細(xì)胞移植、類器官培養(yǎng)、腫瘤研究等眾多領(lǐng)域備受歡迎。但組織消化過(guò)程中常遇到多種問(wèn)題,例如消化不完全、細(xì)胞死亡率高等。如何克服這些問(wèn)題,其實(shí)消化酶的選擇是關(guān)鍵。 |
| 來(lái)了解組織消化過(guò)程中常用的酶吧~ |
|
1.胰蛋白酶 |
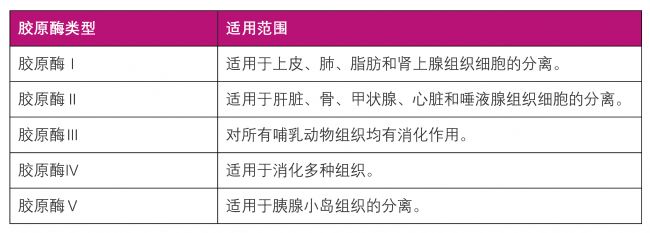 |
| 膠原酶類型及適用范圍表 |
|
3.透明質(zhì)酸酶 |
 |
| 表一:正常組織消化用酶列表 |
 |
| 表二:腫瘤組織消化用酶列表 |
|
參考文獻(xiàn) 1. Kasai-Brunswick TH., et al., (2017) Cardiosphere-derived Cells Do Not Improve Cardiac Function in Rats With Cardiac Failure. Stem Cell Res Ther. Feb 15;8(1):36. 2. Huch.M., et al., (2015) Long-term Culture of Genome-Stable Bipotent Stem Cells From Adult Human Liver. Cell. Jan 15;160(1-2):299-312. 3. Holt PG., et al., (1986) Extraction of Immune and Inflammatory Cells From Human Lung Parenchyma: Evaluation of an Enzymatic Digestion Procedure. Clin Exp Immunol. Oct;66(1):188-200. 4. Campbell AM., et al., (1993) Modulation of Eicosanoid and Histamine Release From Human Dispersed Lung Cells by Terfenadine. Allergy. Feb;48(2):125-9. 5. Sanchez-Romero N., et al., (2020) A Simple Method for the Isolation and Detailed Characterization of Primary Human Proximal Tubule Cells for Renal Replacement Therapy. Int J Artif Organs. Jan;43(1):45-57. 6. Ataollahi F., et al., (2014) New Method for the Isolation of Endothelial Cells From Large Vessels. Cytotherapy. Aug;16(8):1145-52. 7. Leelatian N., et al., (2017) Single cell analysis of human tissues and solid tumors with mass cytometry. Cytometry B Clin Cytom. Jan;92(1):68-78. 8. Roberts EG., et al., (2019) Evaluation of Placental Mesenchymal Stem Cell Sheets for Myocardial Repair and Regeneration. Tissue Eng Part A Jun;25(11-12):867-877. 9. Jankovic-Karasoulos T., et al., (2018) Isolation of villous cytotrophoblasts from second trimester human placentas. Placenta. Dec 15;74:55-58. 10. Tang YL., et al., (2007) A Novel Two-Step Procedure to Expand Cardiac Sca-1+ Cells Clonally. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. Aug 10;359(4):877-83. 11. Meyer J. ., et al., (2016) An optimized method for mouse liver sinusoidal endothelial cell isolation. Exp Cell Res. Dec 10;349(2):291-301. 12. Nakano H., et al., 1799 (2018) Isolation and Purification of Epithelial and Endothelial Cells from Mouse Lung. Methods Mol Biol.:59-69. 13. Jain R. ., et al., (2014) Isolation of thymic epithelial cells and analysis by flow cytometry. Curr Protoc Immunol. Nov 3;107:3.26.1-3.26.15. 14. Tran LS., et al., (2018) Isolation of Mouse Primary Gastric Epithelial Cells to Investigate the Mechanisms of Helicobacter Pylori Associated Disease. Methods Mol Biol. 1725:119-126. 15. De Clercq K., et al., (2017) Isolation of Mouse Endometrial Epithelial and Stromal Cells for In Vitro Decidualization. J Vis Exp Mar 2;(121):55168. 16. Sharon, Y., et al., (2013) Isolation of Normal and Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts from Fresh Tissues by Fluorescence Activated Cell Sorting (FACS). J Vis Exp 71, e4425. 17. Zhang Q., et al., (2016) Isolation and Culture of Single Cell Types from Rat Liver. Cells Tissues Organs. 201(4):253-67. 18. Al-Eisa A., (2017) IgA Enhances IGF-1 Mitogenic Activity Via Receptor Modulation in Glomerular Mesangial Cells: Implications for IgA-Induced Nephropathy. Kidney Blood Press Res.;42(3):391-397. 19. Githens S., et al., (1994) Isolation and Culture of Rhesus Monkey Pancreatic Ductules and Ductule-Like Epithelium Pancreas. Jan;9(1):20-31. 20. Caperna TJ., et al., (2011) Culture of porcine hepatocytes or bile duct epithelial cells by inductive serum-free media In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim. Mar;47(3):218-33. 21. Ataollahi F., et al., (2014) New method for the isolation of endothelial cells from large vessels. Cytotherapy. Aug;16(8):1145-52. 22. Widowati W., et al., (2018) Isolation, Characterization and Proliferation of Cancer Cells from Breast Cancer Patients. Acta Inform Med. Dec;26(4):240-244. 23. Beaupain R., et al., (1993) “Normal” breast cells adjacent to a tumor grown in long-term three-dimensional culture. In Vitro Cellular & Developmental Biology – Plant, 29(2): 100-104. 24. Leung C K., et al., (1982) Morphological and proliferative characteristics of human breast tumor cells cultured on plastic and in collagen matrix. In Vitro Cellular & Developmental Biology – Plant, 18(5): 476-482. 25. Chou J., et al., (2013) Phenotypic and Transcriptional Fidelity of Patient-Derived Colon Cancer Xenografts in Immune-Deficient Mice. PLOS ONE, 8(11). 26. Friedman E., et al., (1981) Tissue culture of human epithelial cells from benign colonic tumors. In Vitro Cellular & Developmental Biology – Plant, 17(7): 632-644. 27. Brattain M G., et al., (1983) Characterization of human colon carcinoma cell lines isolated from a single primary tumour. British Journal of Cancer, 47(3): 373-381. 28. Quatromoni J G., et al., (2015) An optimized disaggregation method for human lung tumors that preserves the phenotype and function of the immune cells. Journal of Leukocyte Biology, 97(1): 201-209. 29. Zhuang X., et al., (2015) Identification of novel vascular targets in lung cancer Br J Cancer. Feb 3; 112(3): 485–494. 30. Welte Y., et al., (2013) Patient Derived Cell Culture and Isolation of CD133+ Putative Cancer Stem Cells from Melanoma. Journal of Visualized Experiments. 31. Tillotson LG., et al., (2001) Isolation, Maintenance, and Characterization of Human Pancreatic Islet Tumor Cells Expressing Vasoactive Intestinal Peptide Pancreas. Jan;22(1):91-8. 32. Nakashiro K., et al., (2004) Phenotypic Switch from Paracrine to Autocrine Role of Hepatocyte Growth Factor in an Androgen-Independent Human Prostatic Carcinoma Cell Line, CWR22R. American Journal of Pathology, 165(2): 533-540. 33. Sheela S., et al., (1990) Angiogenic and invasive properties of neurofibroma Schwann cells. Journal of Cell Biology, 111(2): 645-653. 34. Sacks P G., et al., (1988) Establishment and characterization of two new squamous cell carcinoma cell lines derived from tumors of the head and neck. Cancer Research, 48(10): 2858-2866. 35. Kim M P., et al., (2009) Orthotopic and heterotopic generation of murine pancreatic cancer xenografts [J]. Nature Protocols, 4(11): 1670-1680. 36. Rasheed Z A., et al., (2010) Isolation of Stem Cells from Human Pancreatic Cancer Xenografts. Journal of Visualized Experiments. 37. Vaughan A E., et al., (2011) Lung Cancer in Mice Induced by the Jaagsiekte Sheep Retrovirus Envelope Protein Is Not Maintained by Rare Cancer Stem Cells, but Tumorigenicity Does Correlate with Wnt Pathway Activation. Molecular Cancer Research, 10(1): 86-95. 38. Liu X., et al., (2013) Nonlinear Growth Kinetics of Breast Cancer Stem Cells: Implications for Cancer Stem Cell Targeted Therapy. Scientific Reports , 3(1): 2473-2473. 39. Kazerounian S., et al., (2013) RhoB differentially controls Akt function in tumor cells and stromal endothelial cells during breast tumorigenesis. Cancer Research, 73(1): 50-61. 40. Mazzoleni S., et al., (2013) Gene Signatures Distinguish Stage-Specific Prostate Cancer Stem Cells Isolated From Transgenic Adenocarcinoma of the Mouse Prostate Lesions and Predict the Malignancy of Human Tumors. Stem Cells Translational Medicine, 2(9): 678-689. 41. Duarte S., et al., (2013) Preventive Cancer Stem Cell‐Based Vaccination Reduces Liver Metastasis Development in a Rat Colon Carcinoma Syngeneic Model. Stem Cells, 31(3): 423-432. 42. Gazdar A F., et al., (1980) Continuous, clonal, insulin- and somatostatin-secreting cell lines established from a transplantable rat islet cell tumor. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 77(6): 3519-3523. 43. Sharma N K., et al., (1999) A Novel Immunological Model for the Study of Prostate Cancer. Cancer Research, 59(10): 2271-2276. |
 |
聯(lián)系電話:40000 53055,0512 6832 5983
E-mail:peprotech.infochina@thermofisher.com
- PCL-PVAc-PEG在活性物遞送和生物材料上的應(yīng)用優(yōu)勢(shì)
- PROTAC連接子中作用機(jī)制及氮雜環(huán)的結(jié)構(gòu)優(yōu)勢(shì)與功能特性
- OK432在腫瘤和免疫研究中的作用機(jī)制及應(yīng)用優(yōu)勢(shì)
- 鐵調(diào)素Hepcidin-25作為鐵代謝和免疫反應(yīng)關(guān)鍵調(diào)節(jié)因子的功能和作用
- 糖蛋白Fibronectin在細(xì)胞培養(yǎng)中的功能及作用
- TDP-43的結(jié)構(gòu)與功能及在漸凍癥(ALS)等神經(jīng)退行性疾病中的作用機(jī)制
- DNP-BSA(2,4-二硝基苯偶聯(lián)牛血清白蛋白)在免疫學(xué)研究與檢測(cè)中的作用
- AbMole LPS(脂多糖)在免疫激活、動(dòng)物造模等方面的應(yīng)用及案例分享
- MCE中國(guó)將攜試劑產(chǎn)品亮相美國(guó)芝加哥2025 AACR年會(huì)
- 2024年"MCE中國(guó)生命科學(xué)研究促進(jìn)獎(jiǎng)"評(píng)獎(jiǎng)結(jié)果公布
- 陶術(shù)生物直播預(yù)告:受體藥理學(xué)與藥物發(fā)現(xiàn)研究
- 安捷倫免疫組化法PD-L1檢測(cè)試劑盒獲得歐盟IVDR認(rèn)證
- 德國(guó)Massive Photonics推出多款DNA-PAINT各系試劑盒
- 天隆自主研發(fā)HCV核酸檢測(cè)試劑盒獲批藥監(jiān)局三類NMPA
- 蘭博利德推出新品高保真快速擴(kuò)增 PCR mix試劑盒
- IPHASE邀您共赴BIOCHINA2025第十屆易貿(mào)生物產(chǎn)業(yè)大會(huì)