組蛋白甲基化介紹與作用
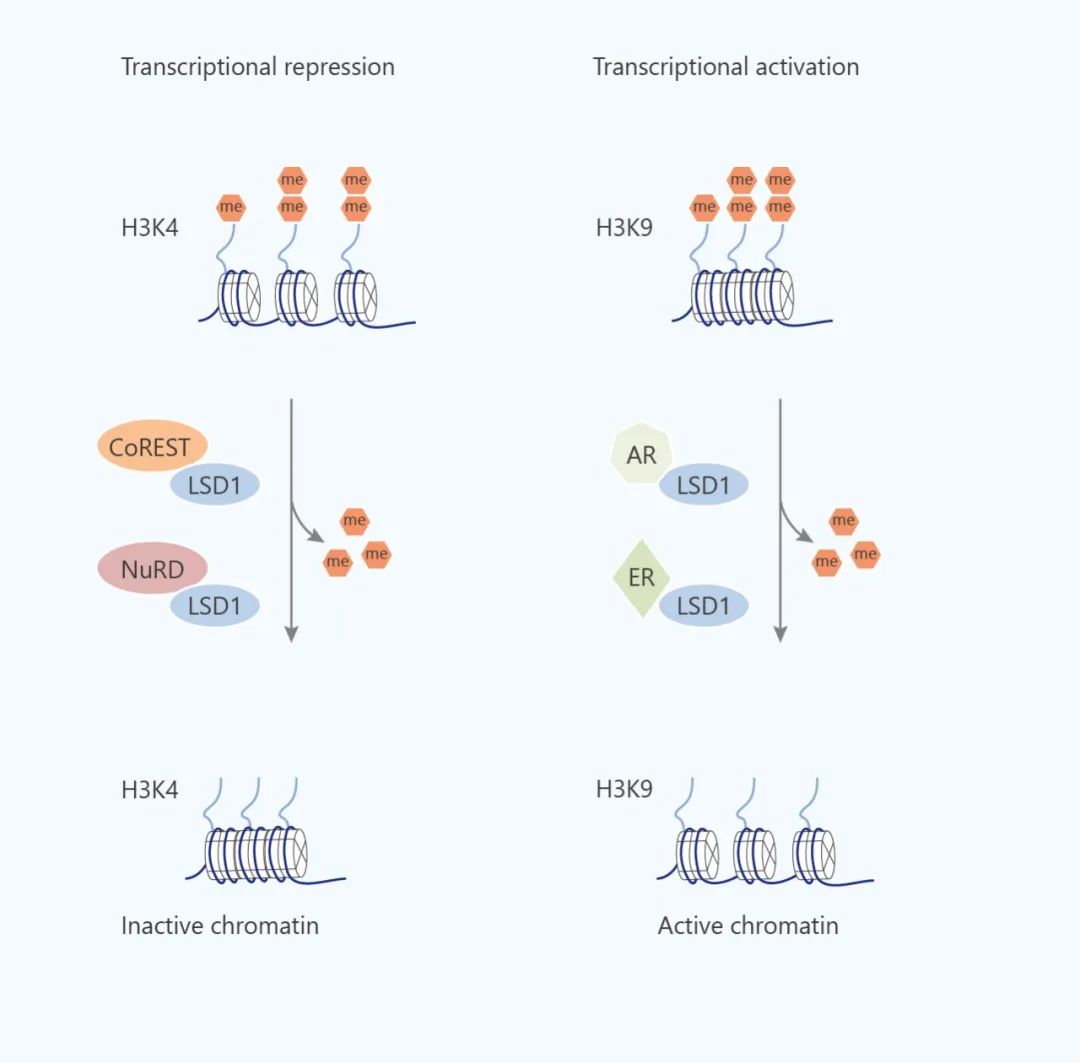
HMTs 和 HDMs 調節基因表達的實例
寫入: 組蛋白甲基轉移酶 (HMTs)
組蛋白甲基轉移酶 (HMTs) 分為兩類:賴氨酸甲基轉移酶 (KMTs) 和精氨酸甲基轉移酶 (PRMTs)。
KMTs 根據催化結構域序列,可分為含 SET 結構域和非 SET 結構域。SET 結構域是組蛋白甲基轉移酶的重要結構域,也是大多數轉移酶含有的結構域,負責甲基轉移酶的酶促活性,包括 SUV39, SET1, SET2, EZH (著名的 EZH2 就在這個家族啦, 可對 H3K27 進行單,二和三甲基化),RIZ (PRDM, SMYD, SUV420) 等家族。而不含 SET 結構域的蛋白較少,如 DOT1L 蛋白。DOT1L 是已知的靶向組蛋白 H3K79 位置的組蛋白甲基轉移酶。H3K79 位于組蛋白 H3 的球狀結構域中,但它暴露在核小體表面上,在這里它可以被 DOT1L 甲基化。因此,DOT1L 的催化發生在核小體表面而不是 N 末端尾巴上。
PRMTs 根據其催化活性可分為三類,催化精氨酸的單甲基化 (MMA),不對稱 (ADMA) 或對稱二甲基化 (SDMA)。I 型 PRMTs (PRMT1, PRMT2, PRMT3, PRMT4, PRMT6 和 PRMT8) 產生單或不對稱二甲基化精氨酸 (ADMA),II 型 PRMTs (PRMT5 和 PRMT9) 產生單或對稱二甲基化精氨酸 (SDMA)。而 Ⅲ 型的 PRMT7,只產生 MMA。組蛋白甲基化轉移酶的成員實在不少,并有各自的識別位點,就列在樹上給小伙伴們看吧。
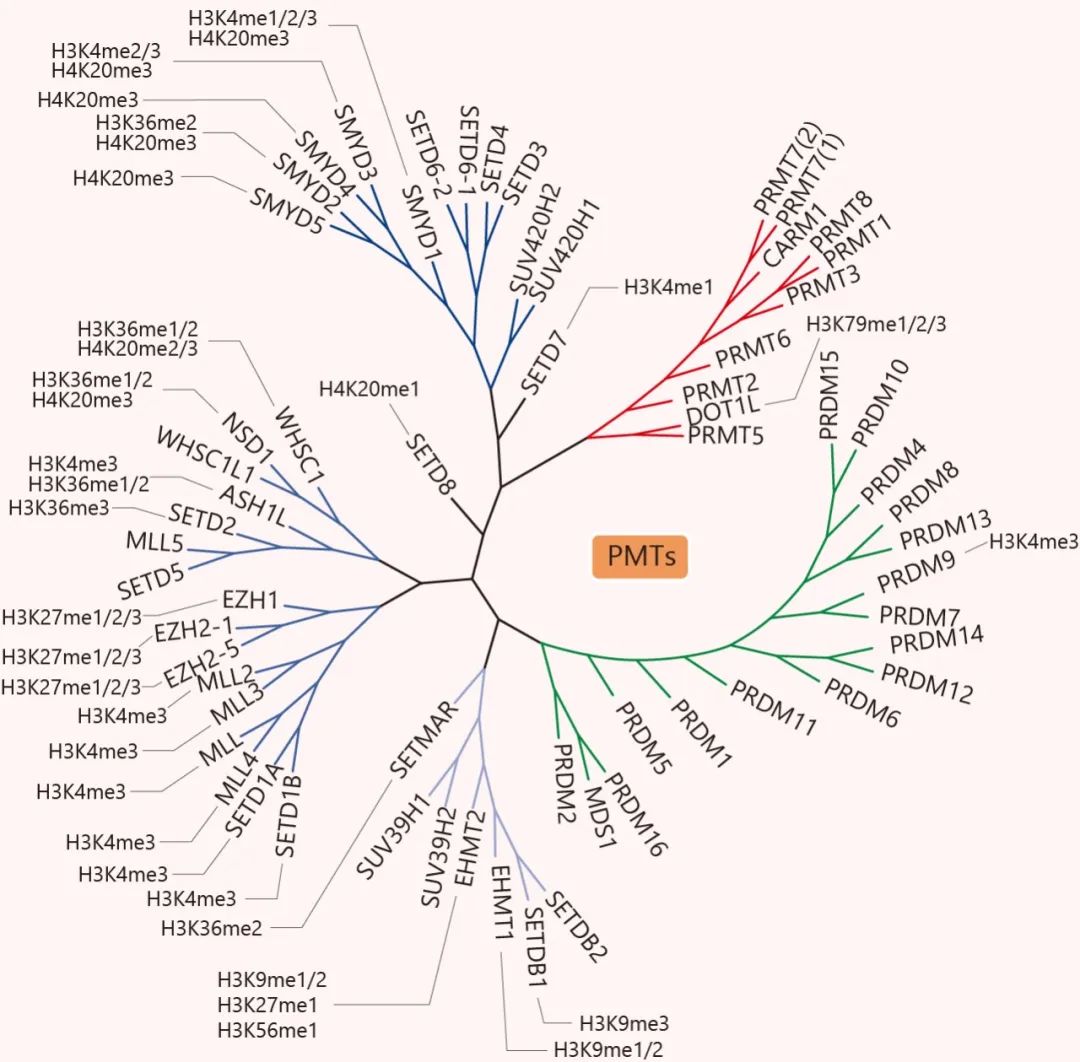
蛋白甲基轉移酶的系統發育樹
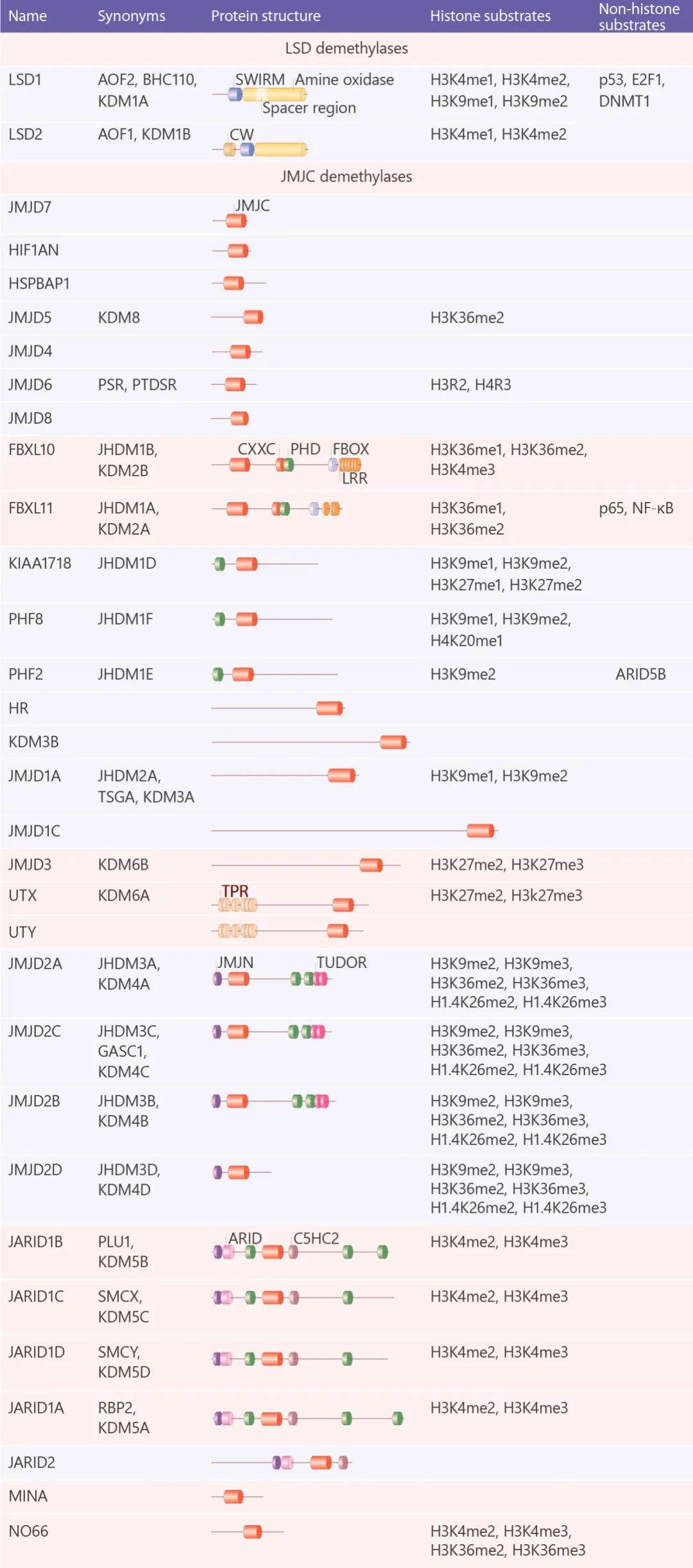
擦除: 組蛋白脫甲基酶 (HDMs)組蛋白去甲基化酶與轉移酶的作用相反。組蛋白去甲基酶既能靶向組蛋白又能靶向非組蛋白底物。目前已經鑒定出兩個進化上保守的組蛋白去甲基化酶家族:賴氨酸特異性去甲基化酶 (LSD) 和 Jumonji C (JMJC) 蛋白家族,它們利用不同的反應機理來去甲基。
LSD 蛋白家族由 LSD1 和 LSD2 組成,它們通過 FAD 依賴的胺氧化反應 (flavin adenine dinucleotide-dependent amineoxidase) 對單和二甲基化的賴氨酸殘基進行脫甲基化。其中 LSD1 (KDM1A) 是第一個發現的組蛋白賴氨酸脫甲基酶 (KDM), 催化 H3K4me1/2, H3K9me1/2 的脫甲基化,另外,LSD1 也可以對非組蛋白脫甲基化,如 p53 上的 K370me1 和 K370me2, DNMT1 上的 Lys1096 和 E2F1 上的 Lys185。 LSD1 作為轉錄阻遏物和激活物
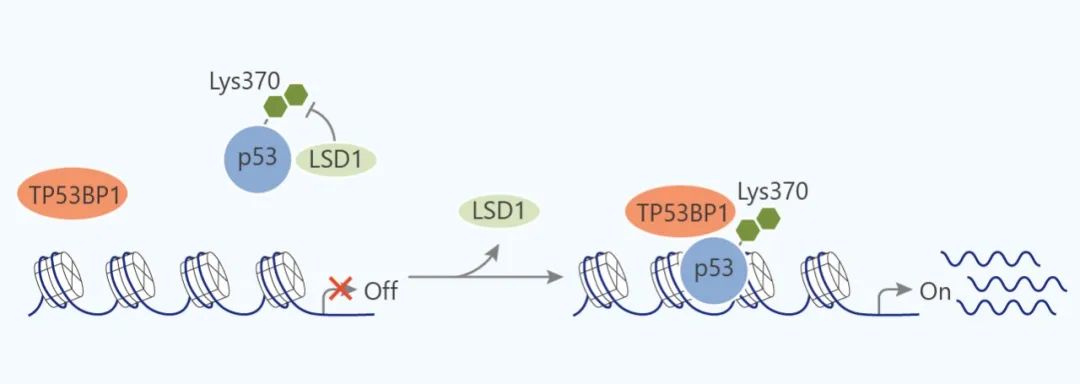
LSD1 對 p53 活性的調節
而 JMJC 家族催化的脫甲基酶反應是一種依賴于鐵 (II) 和 α-酮戊二酸的雙加氧酶 (Fe(II)/α-ketoglutarate-dependent hydroxylase) 反應。這使得 JMJC 家族的酶與 LSD 家族不同,能夠脫三甲基賴氨酸殘基。JMJC 家族由 30 個成員組成,目前為止,這些成員中的 18 個已顯示具有組蛋白脫甲基酶活性。因為組蛋白脫甲基化酶的成員也實在不少,就不一一列舉了,小伙伴們可以參考這個表。 組蛋白去甲基化酶家族[6]
讀取:組蛋白甲基化的識別蛋白
甲基化組蛋白的識別是通過具有甲基結合域的蛋白來實現的,這些結合域包括 ADD, Ankyrin, BAH, Chromobarrel, Chromodomain, Double Chromodomain (DCD), MBT, PHD, PWWP, TTD, Tudor, WD40 以及 zf-CW。其中含 Chromodomain, MBT 重復序列,PWWP, Tudor, DCD 蛋白組成了 Royal 超家族。
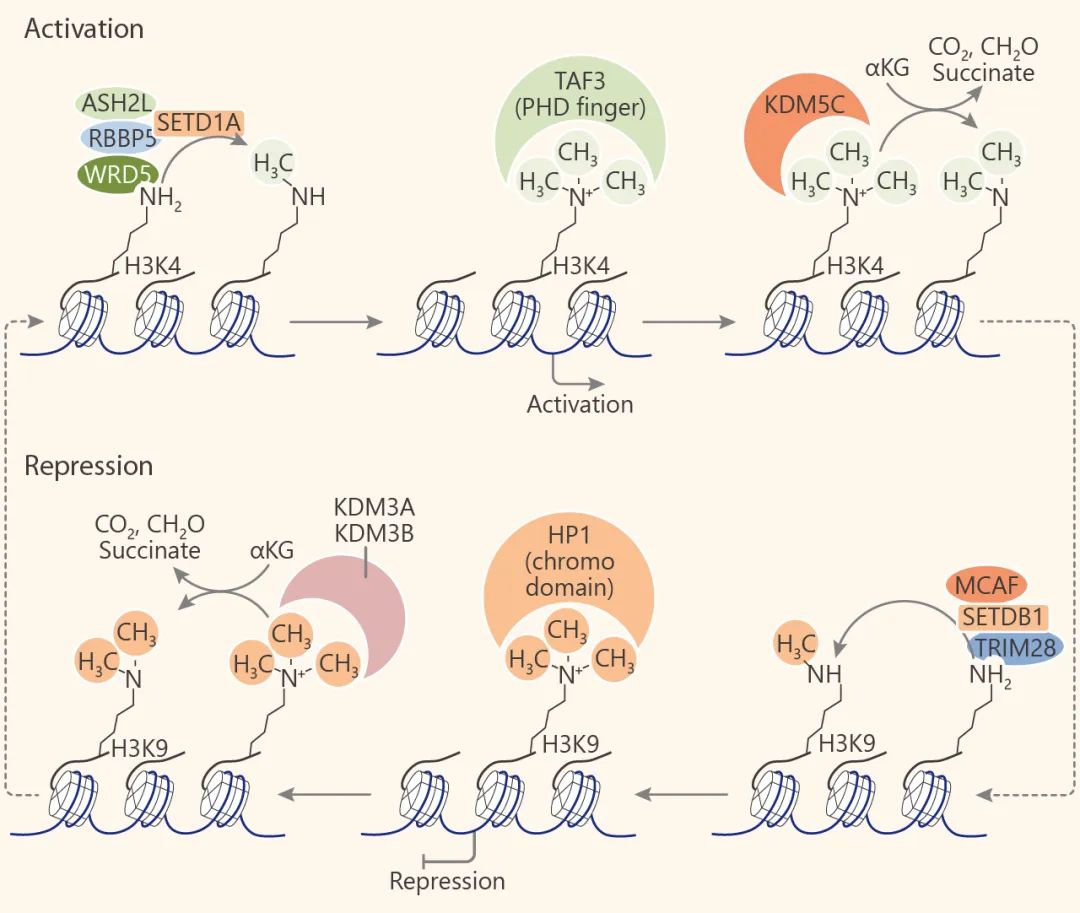
這些域是怎么識別組蛋白甲基化位點呢?許多研究表明,含 Chromodomain 蛋白的 HP1 和 Chd1,分別可以識別 H3K9me 和 H3K27me。而人的 L3MBTL1 蛋白,是已知的轉錄阻遏物,以嚴格依賴組蛋白甲基化標記的方式 (如 H4K20me1/2 和 H1K26me1/2) 壓緊染色質。L3MBTL1 含有三個 MBT 域,都很重要。例如它的第二個 MBT 結構域對 H1K26me1/2 和 H4K20me1/2 的結合很重要。含有 PHD 手指基序的 BPTF, RAG2, PYGO 和 ING2 都可以識別并結合到 H3K4me3。另外,含 WD40 重復序列的蛋白如 WDR5,可通過與 MLL, RBBP5, ASH2L 和 DPY30 形成蛋白質復合物,促進組蛋白 H3K4 甲基化。
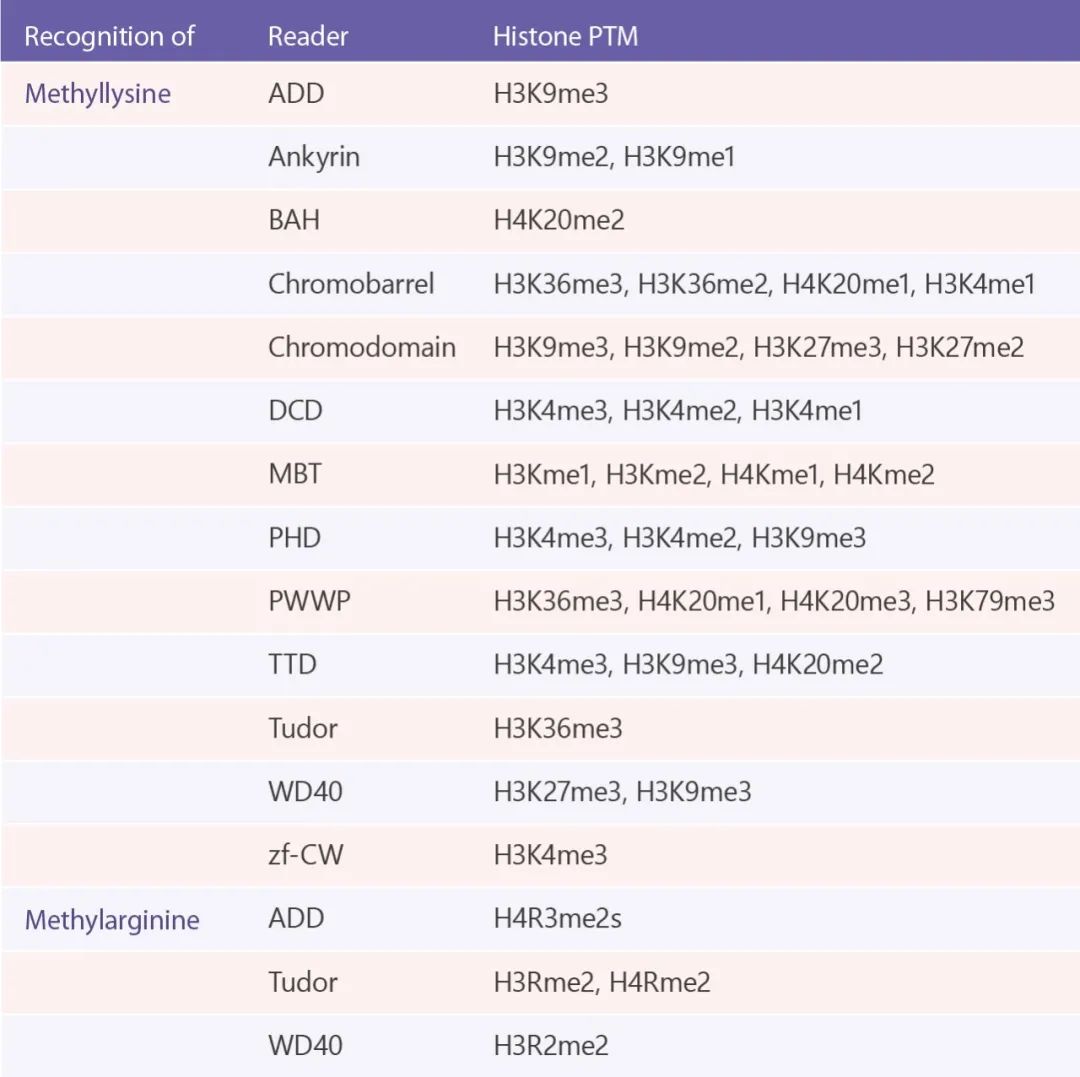
組蛋白甲基化閱讀器 (注: PTM: 蛋白翻譯后修飾)[10]
如同武林高手組合出招一樣,組蛋白甲基化的不同位點和模式可以演化出很多的甲基化修飾模式,增加了受組蛋白甲基化調節的基因表達的復雜性和多樣性。而 HMTs 和 HDMs 小心地維持著組蛋白甲基化的水平,因而也就不難理解它們的失調與癌癥之間密切的關系,如組蛋白甲基轉移酶 NSD1 和 EZH2 在許多腫瘤中過表達,DOT1L 在白血病中有著廣泛的作用等等。組蛋白脫甲基酶 KDM1A, KDM5B 分別在低分化神經母細胞瘤和前列腺癌中過表達。LSD1 與 p53 的直接相互作用會降低 p53 的活性,包括 p21 的表達降低,與腫瘤發生有關等等。另外,對組蛋白甲基化標記的誤讀 (組蛋白甲基化的讀取蛋白活性異常) 也與許多人類疾病有關,包括發育異常以及癌癥。因此,這些蛋白質的小分子抑制劑是有用的化學探針或潛在的治療劑。
部分靶向組蛋白甲基化修飾的蛋白抑制劑| 化合物 | 作用 |
| HMTs | |
| Tazemetostat | 選擇性,具有口服活性的 EZH2 抑制劑,用于治療上皮樣肉瘤;抑制含有 PRC2 復合體的野生型 EZH2 的活性; FDA Approved |
| GSK126 | 有效的,選擇性的 EZH2 甲基轉移酶抑制劑;在體內外明顯抑制腫瘤形成,降低細胞遷移,侵襲,逆轉耐藥 |
| AZ505 | 有效的,具有選擇性的 SMYD2 抑制劑 |
| Pinometostat | 有效的 DOT1L 組蛋白甲基轉移酶抑制劑; Phase 2 |
| EPZ015666 | 有口服活性的 PRMT5 抑制劑 |
| MS023 | 有效的,選擇性的,具有細胞活性的人 I 型蛋白精氨酸甲基轉移酶 (PRMTs) 抑制劑 |
| HDMs | |
| GSK-J4 | 有效的 H3K27me3/me2 脫甲基化酶 JMJD3/KDM6B 和 UTX/KDM6A 雙抑制劑 |
| GSK2879552 | 具有口服活性的,不可逆的 LSD1 抑制劑,具有抗腫瘤活性; Phase 1 |
| Seclidemstat | 有效的 LSD1 抑制劑; Phase 1 |
| JIB-04 | 是 Jumonji 組蛋白脫甲基酶廣譜抑制劑 |
| Reader | |
| UNC 669 | L3MBTL1 和 L3MBTL3 的抑制劑 |
MCE 的所有產品僅用作科學研究,我們不為任何個人用途提供產品和服務
HY-L005 表觀遺傳化合物庫 Epigenetics Compound Library縮寫:
HMTs: histone methyltransferases
HDMs: histone demethylases
PHD: plant homeodomain
PRMTs: protein arginine methyltransferase
KMTs: histone lysine methyltransferases
DOT1L: Dot1-Like histone methyltransferase
MMA: monomethylarginine
ADMA: asymmetric dimethylarginine
SDMA: symmetric dimethylation
LSD: lysine-specific histone demethylase
KDM: histone lysine demethylases
HP1: heterochromatin protein 1
參考文獻
↓ 下滑查看更多文獻
1. Cheng Y, et al. Targeting epigenetic regulators for cancer therapy: mechanisms and advances in clinical trials. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2019 Dec 17;4:62.
2. Jambhekar A, et al. Roles and regulation of histone methylation in animal development. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2019 Oct;20(10):625-641.
3. Xin Yi, et al. Histone methyltransferases: novel targets for tumor and developmental defects. Am J Transl Res. 2015 Nov 15;7(11):2159-75.
4. Tian X, et al. Histone lysine-specific methyltransferases and demethylases in carcinogenesis: new targets for cancer therapy and prevention. Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2013 Jun;13(5):558-79.
5. Michalak EM, et al. s of DNA, RNA and histone methylation in ageing and cancer. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2019 Oct;20(10):573-589.
6. Kooistra SM, et. Molecular mechanisms and potential functions of histone demethylases. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2012 Apr 4;13(5):297-311.
7. Milite C, et al. The emerging role of lysine methyltransferase SETD8 in human diseases. Clin Epigenetics. 2016 Sep 22;8:102.
8. Islam AB, et al. Co-regulation of histone-modifying enzymes in cancer. PLoS One. 2011;6(8):e24023.
9. Huang J, et al. p53 is regulated by the lysine demethylase LSD1. Nature. 2007 Sep 6;449(7158):105-8.
10. Musselman CA, et al. Perceiving the epigenetic landscape through histone readers. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2012 Dec;19(12):1218-27.
11. Zhu H, et al. Molecules. 2020 Jan 29;25(3). pii: E578.Small Molecules Targeting the Specific Domains of Histone-Mark Readers in Cancer Therapy.
12. Albert M, et al. Histone methyltransferases in cancer. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2010 Apr;21(2):209-20.
13. D'Oto A, et al. Histone demethylases and their roles in cancer epigenetics. J Med Oncol Ther. 2016;1(2):34-40.
14. Arrowsmith CH, et al. Epigenetic protein families: a new frontier for drug discovery. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2012 Apr 13;11(5):384-400.
15. McCabe MT, et al. Targeting Histone Methylation in Cancer. Cancer J. 2017 Sep/Oct;23(5):292-301.
16. Magliulo D, et al. Lysine-Specific Demethylase 1A as a Promising Target in Acute Myeloid Leukemia.Front Oncol. 2018 Jul 19;8:255.